- Home
- /
- Health Conditions
- /
- Constipation
Constipation treatment
4.6/5 based on 28000+ reviews
How our doctors can help
See a doctor now
From $39
Request a certificate
From $14.90
Request a referral
From $39
Request a script
From $18.90

When to consult a doctor for constipation?
If constipation is persistent or worsening
See a doctor if constipation lasts longer than usual, does not improve with dietary or lifestyle changes, or if you notice a sudden, unexplained change in your normal bowel habits.
If you experience pain or additional symptoms
Consult a medical practitioner if constipation is accompanied by severe abdominal pain or cramping, nausea, vomiting, or a persistent feeling of fullness.
If there are warning signs
Consult a doctor urgently if you notice blood in your stool or experience unexplained weight loss along with constipation, as these may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
This guide does not replace professional care. Consult a doctor to manage your symptoms. In emergencies, call 000. The content is research-backed & medically reviewed by Dr. Ammar AL-ANI, MBChB, CCBST, AMC.
Causes and symptoms
Constipation causes
- Dietary factors: A low-fibre diet, insufficient water intake, or inadequate nutrition.
- Lack of physical activity: Sedentary lifestyles can reduce bowel movement frequency.
- Stress and anxiety: Emotional stress can disrupt normal digestion.
- Medical conditions and meds: Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), hypothyroidism, diabetes, or neurological disorders and certain medications can affect bowel function.
- Ignoring the urge to go: Regularly ignoring the urge to have a bowel movement can disrupt normal bowel rhythms.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can slow down the digestive system.
- Ageing: Older adults may experience slower bowel movements due to reduced muscle tone and other age-related changes.
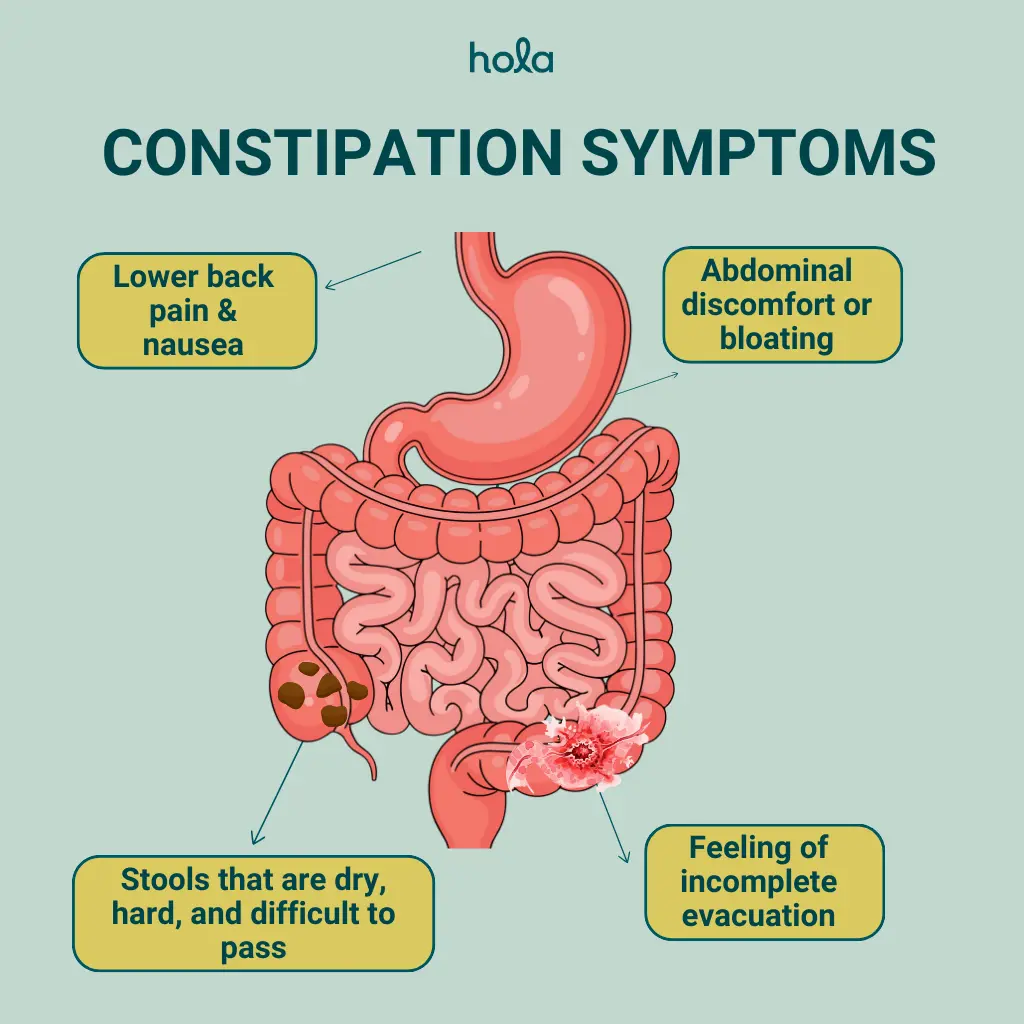
Constipation symptoms
- Infrequent bowel movements: Having less than three bowel movements per week.
- Straining: Difficulty or pain when trying to pass stools.
- Hard or lumpy stools: Stools that are dry, hard, and difficult to pass.
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation: A sensation that you haven’t fully emptied your bowels.
- Abdominal discomfort or bloating: Feeling of fullness, bloating, or cramps in the abdomen.
- Lower back pain: Some individuals may experience aching or pain in the lower back.
- Nausea: Feeling nauseous, especially if constipation is severe or chronic.
Prevention and treatment
Constipation is a common condition in Australia, affecting a significant portion of the adult population. It is estimated that approximately 24% of Australian adults experience chronic constipation. Additionally, about 40% of adults report sub-chronic constipation. The prevalence of constipation can vary based on factors such as age, gender, and lifestyle. Here are some prevention steps to be taken after your GP consult-
Constipation symptoms
- Increase fibre intake: Eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can help soften stools and promote regular bowel movements. Foods high in fibre, like prunes, apples, and spinach, are especially beneficial.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps soften stools and prevents dehydration, which can worsen constipation.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity stimulates bowel movements. Even simple activities like walking or yoga can be effective.
- Use natural laxatives: Certain natural remedies like prunes, psyllium husk, or flaxseeds can act as mild laxatives and help relieve constipation.
- Try warm liquids: Drinking warm water, herbal teas (e.g., peppermint or ginger), or warm lemon water in the morning can help stimulate digestion.
- Establish a routine: Setting aside regular time each day to use the bathroom can help train your body to have consistent bowel movements.
- Avoid delaying the urge: When you feel the urge to go, try not to ignore it, as this can worsen constipation over time.
Hola Health provides a fast and convenient way for you to see a doctor online in minutes, 24/7 across Australia. Much like an in-person GP clinic, our AHPRA-registered Australian online GP chat will conduct a comprehensive assessment to provide the best possible care, instantly.

Speak to our doctors 24/7
Providing consults for
Helpful resources
Download our Mobile App for better performance
- Book appointments instantly.
- Stay connected wherever you are.
- Experience healthcare, uninterrupted.
 Scan the QR Code to download the app instantly
Scan the QR Code to download the app instantly