- Home
- /
- Health Conditions
- /
- Boils
Boils Treatment
A boil is a painful, pus-filled bump that forms under the skin, usually caused by a bacterial infection. Connect with an AHPRA-accredited online doctor to manage boils symptoms within minutes from anywhere in Australia, 24/7.
4.6/5 based on 28000+ reviews
How our doctors can help
See a doctor now
From $39
Request a certificate
From $14.90
Request a referral
From $39
Request a script
From $18.90
When to consult a doctor for boils?
Signs of a spreading infection
Look for spreading redness, warmth, and swelling. If you develop a fever or chills, this is a sign that the infection may have entered your bloodstream and requires urgent care.
If the boil is in a sensitive area
As these spots are more prone to complications. Additionally, if the boil feels "stuck" and does not burst or drain on its own after several days of warm compresses, consult a GP.
If you develop several boils at once
It may signal a recurring bacterial issue. It is especially important to seek advice early if you have a weakened immune system or a condition like diabetes, as your body may struggle to fight the infection without antibiotics.
This guide does not replace professional care. Consult a doctor to manage your symptoms. In emergencies, call 000 or visit a hospital immediately. The content is research-backed & medically reviewed by Dr Vishnu Gopalan, Co-Founder & Chief Medical Officer at Hola.
Boils causes and symptoms
Causes of boils
Boils are primarily caused by a bacterial infection, most commonly by Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria that naturally lives on the skin and in the nose. When the bacteria enter a hair follicle or sweat gland through a cut or break in the skin, they can cause an infection that leads to the formation of a boil.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing boils, including:
- Poor hygiene: Not washing regularly can increase the likelihood of bacteria spreading.
- Weakened immune system: Conditions like diabetes, HIV, or medications that suppress the immune system can make the body more susceptible to infections.
- Skin irritation or injury: Frequent friction, sweating, or scratching can create openings for bacteria.
- Existing skin conditions: Conditions like acne or eczema can increase the risk.
- Contact with infected individuals: Boils are contagious, so skin-to-skin contact can spread bacteria.
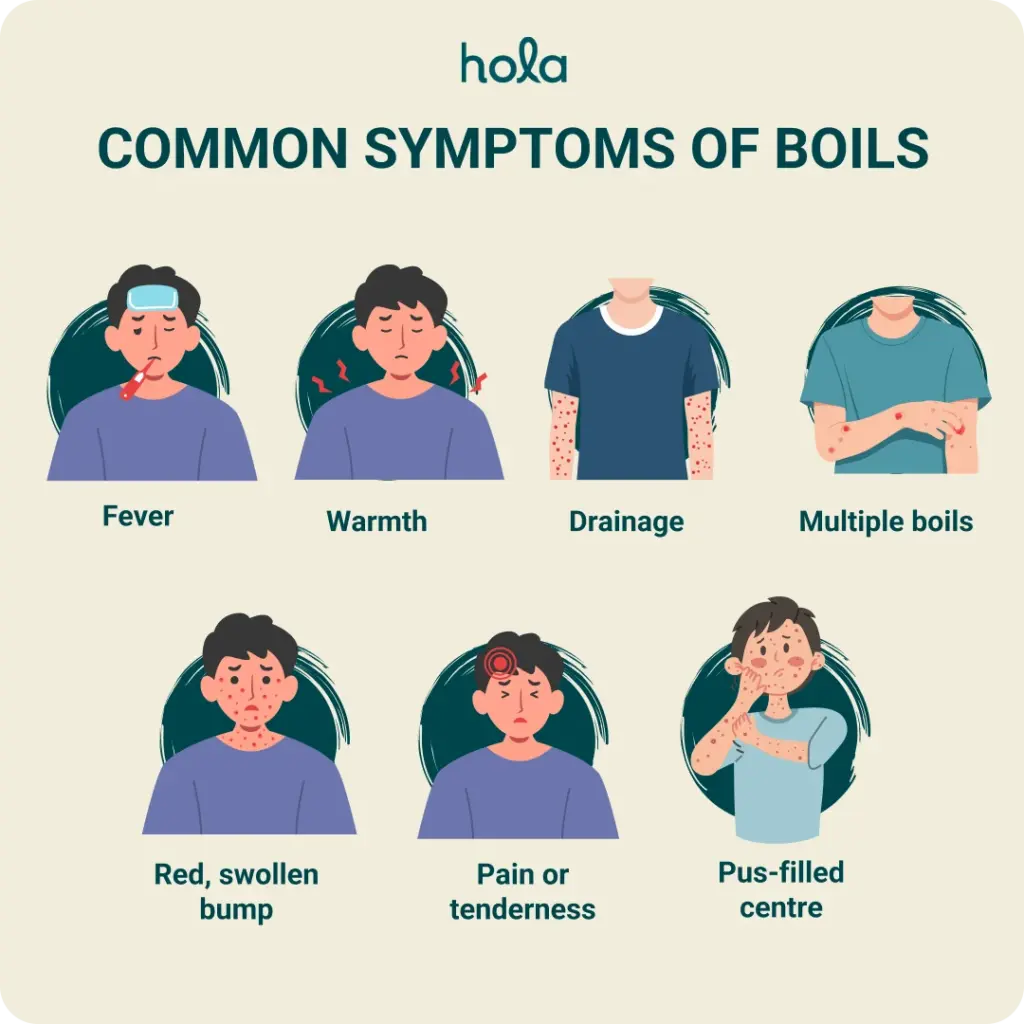
Symptoms of boils
- Red, swollen bump: The area around the boil becomes red and inflamed. The bump starts as a small, tender, and hard lump.
- Pain or tenderness: The area around the boil is usually painful to the touch, especially as it grows.
- Pus-filled centre: As the infection progresses, the boil may develop a white or yellow centre filled with pus.
- Warmth: The skin around the boil may feel warm to the touch due to the infection.
- Fever: In some cases, a boil may cause fever, indicating the infection may be spreading or more severe.
- Drainage: Once the boil bursts or is drained, you may notice thick, yellow or green pus draining from the bump.
- Multiple boils: Sometimes, a cluster of boils (called a carbuncle) may form, leading to a more widespread infection.
Treatment and prevention
To prevent boils, focus on keeping your skin clean, dry, and free from irritation. Practice good hygiene by washing your hands regularly and using antibacterial soap on areas prone to breakouts. Avoid sharing personal items like towels or razors to stop the spread of bacteria. You should also wear loose-fitting clothing to prevent friction and be extra careful during activities like waxing or shaving to avoid small skin injuries. Managing your overall health is just as important. If you have a boil, some home remedies after GP consult may help alleviate discomfort and promote healing
- Warm compress: Apply a warm, moist cloth to the affected area for 20-30 minutes, several times a day. The heat helps increase blood flow and encourages the boil to drain naturally.
- Tea tree oil: Known for its antibacterial properties, tea tree oil may help reduce infection. Dilute a few drops with a carrier oil (like coconut oil) and apply it to the boil with a cotton ball.
- Epsom salt bath: Adding Epsom salt to a warm bath may help reduce swelling and draw out the infection. Soak the affected area for 15-20 minutes.
- Turmeric: Turmeric has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. You can apply a paste made from turmeric powder and water to the boil or take it as a supplement. Consult a doctor before use.
- Aloe vera: Aloe vera gel has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties. Apply fresh aloe vera gel to the boil to reduce swelling and pain.
Hola Health provides a fast and convenient way for you to see a doctor online in minutes, 24/7 across Australia. Much like an in-person GP clinic, our AHPRA-registered online GP appointment will conduct a comprehensive assessment to provide the best possible care, instantly.

Speak to our doctors 24/7
Providing consults for
Helpful resources
Download our Mobile App for better performance
- Book appointments instantly.
- Stay connected wherever you are.
- Experience healthcare, uninterrupted.
 Scan the QR Code to download the app instantly
Scan the QR Code to download the app instantly 

