Diarrhoea at night (nocturnal diarrhoea): Causes, & treatment
Written by the editorial staff writer at Hola. Medically Reviewed by Dr. Ammar AL-ANI, MBChB, CCBST, AMC.

Contents

What is nocturnal diarrhoea (diarrhoea at night)?
Nocturnal diarrhoea is characterised by episodes of diarrhoea that occur during the night, often disrupting a person’s sleep. In contrast to typical daytime diarrhoea, which is frequently associated with dietary factors or mild infections, night-time diarrhoea is of greater concern as it may reflect a more serious medical issue. Some prevalent causes include inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, infections, complications related to diabetes, microscopic colitis, and malabsorption disorders. It is less commonly attributed to functional conditions like irritable bowel syndrome. Ongoing nocturnal diarrhoea requires medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and initiate treatment.Symptoms of nocturnal diarrhoea
Symptoms associated with nocturnal diarrhoea consist of frequent, urgent bowel movements that disturb sleep during the night. The stools are usually loose or watery and may be accompanied by abdominal cramping, bloating, or discomfort. In certain situations, additional symptoms such as fever, fatigue, weight loss, or blood in the stool may be present, particularly if the diarrhoea stems from an underlying condition like inflammatory bowel disease or infection. Chronic nocturnal diarrhoea can also result in dehydration and interrupted sleep.Experiencing these symptoms? Speak with a doctor within 15 minutes.
What causes diarrhoea at night?
Nighttime diarrhoea, or nocturnal diarrhoea, can arise from various underlying conditions. Typical causes include inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which provoke persistent inflammation in the digestive system. Infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites may also result in bowel movements at night. Diabetes, especially when complicated by nerve damage (autonomic neuropathy), can affect bowel control and lead to diarrhoea. Other potential causes include microscopic colitis, malabsorption issues like lactose intolerance or coeliac disease, and side effects from medications or diabetes drugs.What are the treatment options for nocturnal diarrhoea?
Treatment for nocturnal diarrhoea is based on the underlying cause, with the aim to alleviate symptoms, address the primary condition, and prevent complications like dehydration or interrupted sleep.- Infections: When caused by bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections, treatment typically involves specific antimicrobial therapies. Antibiotics can be prescribed for bacterial infections, whereas antiparasitic medications are used for conditions like giardiasis.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Management for conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis may include anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or biologic treatments, depending on the severity of the illness.
- Microscopic colitis: This type of colitis is generally treated with medications, along with dietary adjustments and the avoidance of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which may aggravate symptoms.
- Malabsorption disorders: For conditions like lactose intolerance or coeliac disease, dietary changes are essential. Eliminating lactose or gluten from the diet can help manage diarrhoea and enhance overall digestion.
- Medication-induced diarrhoea: If diarrhoea occurs as a side effect of medications like antibiotics or metformin, doctors may modify the dosage, change medications, or prescribe additional treatments to alleviate symptoms.
- General supportive care: Regardless of the underlying cause, it is crucial to maintain hydration and balance electrolytes. Oral rehydration solutions and, in certain instances, anti-diarrhoeal medications like loperamide might be suggested under medical guidance.
Prevention tips for diarrhoea at night
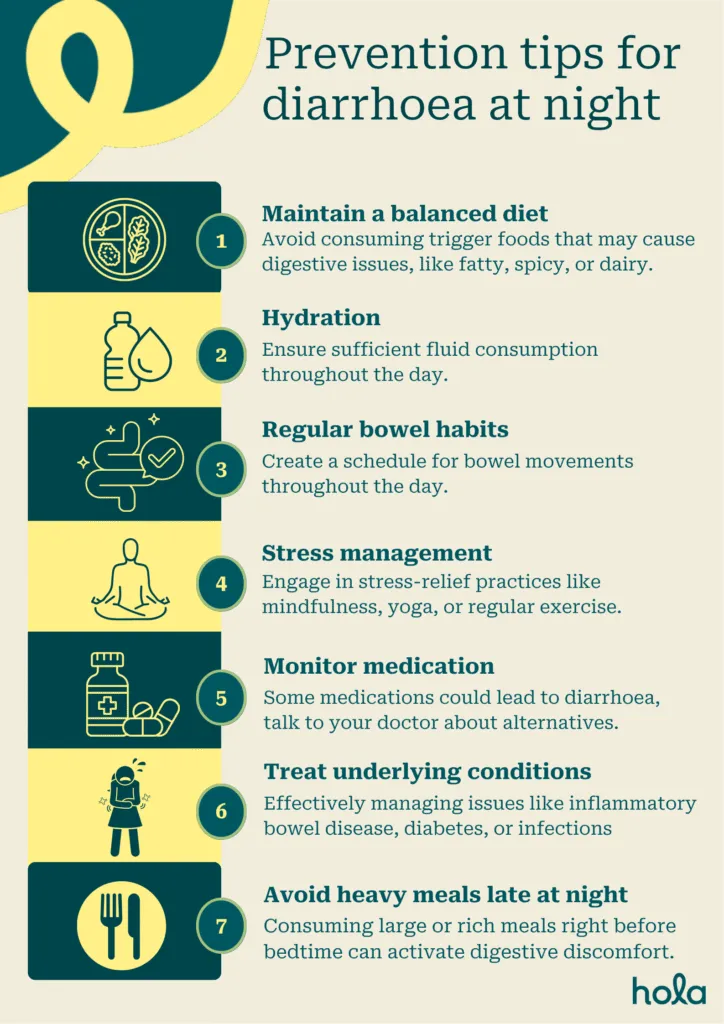
To minimise the risk of nocturnal diarrhoea, several preventative steps can be implemented:- Maintain a balanced diet: Avoid consuming trigger foods that may cause digestive problems, such as fatty, spicy, or dairy products (particularly for those who are lactose intolerant). For individuals with malabsorption conditions, it is important to eliminate gluten or other irritants as per a healthcare provider’s recommendations.
- Stay hydrated: Ensure sufficient fluid consumption throughout the day, particularly if there is a history of diarrhoea, to avoid dehydration.
- Manage stress: Ongoing stress can worsen digestive problems, such as nocturnal diarrhoea. Engage in stress-relief practices like mindfulness, yoga, or regular exercise.
- Regular bowel habits: Create a schedule for bowel movements throughout the day, which can help stabilise digestion and lower the chance of nighttime occurrences.
- Monitor medications: If you are taking medications that could lead to diarrhoea, talk to your doctor about whether alternatives or changes are needed.
- Treat underlying conditions: Effectively managing issues like inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes, or infections can help avoid instances of nocturnal diarrhoea. Regular check-ups and following prescribed treatments are vital.
- Avoid heavy meals late at night: Consuming large or rich meals right before bedtime can activate digestive discomfort and heighten the likelihood of nocturnal diarrhoea. Try to eat your last meal at least 2-3 hours before going to sleep.
If your symptoms persist, worsen overnight, or you are concerned about dehydration, consider speaking with an after-hours online GP for timely medical advice.
When to speak to a doctor for diarrhoea at night
You should reach out to a GP if nocturnal diarrhoea continues for several days, is accompanied by severe dehydration, fever, weight loss, blood in the stool, or intense abdominal pain. If it greatly interrupts your sleep, causes chronic fatigue, or is associated with medication side effects, it’s important to seek medical advice. Furthermore, if you have existing health conditions like diabetes or gastrointestinal disorders, consulting a doctor is crucial to avoid complications and receive appropriate care. Online doctors can help in giving quick consults, instant medical certificates, instant scripts online and online referrals.Conclusion
Bathroom runs at night aren’t just a sleep-stealer; they may be your gut’s way of signalling a problem. Understanding the underlying cause and finding the right solution can bring relief and better rest.FAQs
Is it normal to have diarrhoea in the middle of the night?
Occasional diarrhoea at night can happen, especially after a heavy or questionable meal. But if it becomes a frequent pattern, it’s not considered normal and may signal an underlying issue like an infection, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or another digestive issue. It’s wise to consult a healthcare professional if it keeps recurring.Can lactose intolerance cause nocturnal diarrhoea?
Yes, consuming dairy products in the evening or before bed can trigger nighttime diarrhoea if you are lactose intolerant. The inability to process lactose may result in symptoms such as gas, bloating, and loose stools, which can disrupt sleep.How to stop nocturnal diarrhoea?
To prevent nocturnal diarrhoea, it’s important to identify and treat the underlying cause. Avoid trigger foods like caffeine, dairy, and spicy meals. At night, have earlier dinners, drink plenty of fluids, and manage stress. If symptoms persist, consult a doctor for further evaluation and care.Can anxiety cause nocturnal diarrhoea?
Yes, anxiety can cause digestive problems, including nocturnal diarrhoea. Stress and anxiety can affect digestion, leading to diarrhoea, especially at night when your body is relaxed. Stress management through relaxation exercises or therapy can help alleviate these symptoms.Why does my diarrhoea get worse at night?
Diarrhoea may worsen at night due to several factors, including the body’s natural circadian cycle, which can impact digestion. Stress or anxiety tends to increase at night, making symptoms worse. Additionally, certain foods or medications taken in the evening may aggravate the digestive system. If it persists, consult a doctor for a clear diagnosis.What causes diarrhoea while sleeping?
Diarrhoea while sleeping can be caused by conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), infections, or food intolerances such as lactose. Stress and anxiety can also exacerbate symptoms during the night. Additionally, digestive processes may slow down during sleep, leading to discomfort or sudden urges. If it happens often, seeking medical advice is essential.Need time off to recover? Get your medical certificate online within 15 minutes.
What we treat
- Cough
- Nausea & vomiting
- Fever
- Hayfever
- Fatigue
- Sore throat
- Acne
- Hair loss
- Gout
- Eczema
- Rosacea
- Sunburn
- UTI
- Erectile dysfunction
- Contraception
- Morning sickness
- Morning after pill
- Prostate health
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Stress
- Grief & loss
- Antidepressants
- Premature ejaculation
- Asthma
- Blood pressure
- Blood thinners
- Diabetes
- Cholesterol
- Migraines & headaches
- Allergies
- Body ache
- Heartburn & reflux
- Sleep disorder
- Pain relief
- Gastro
Related Articles
Disclaimer
This blog is for general informational purposes only and does not indicate that Hola Health provides all treatments or preventive measures mentioned. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified health professional with any questions you may have regarding your health or a medical condition. For emergencies please immediately contact 000. Any medical topics discussed are intended to educate, not to imply availability through Hola Health.
 Facebook
Facebook  X
X  Copy Link
Copy Link